The Warning Signs of Gum Disease
Periodontitis, also known as gum disease or periodontal disease, starts with bacterial development in your mouth. It can lead to tooth loss if not treated because it damages the tissue surrounding your teeth.
How Does Gum Disease Start?
The main factor for gum disease is plaque. Periodontal disease, nevertheless, can also be caused by other things. These comprise:
Gums become more sensitive as a result of hormonal changes, such as those that take place during pregnancy, adolescence, menopause, and monthly menstruation, which makes gingivitis more likely to develop.
Illnesses might impact the state of your gums, which includes immune-system-interfering diseases like cancer or HIV. Patients with diabetes are more likely to acquire infections, such as periodontal disease and cavities, since diabetes impairs the body's capacity to use blood sugar.
The saliva flow, which protects teeth and gums, can be decreased by several medications, impacting oral health. Certain medications, including the anticonvulsant Dilantin and the angina medications Procardia and Adalat, might result in aberrant gum tissue growth.
Destructive behaviors like smoking hamper the ability of gum tissue to heal itself.Gingivitis is more likely to form when oral hygiene practices are poor, such as not brushing and flossing every day. Gingivitis can occur for various reasons, including a family history of dental disease.
What Symptoms And Signs Point to Gum Disease?
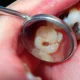
Gum disease can progress even in its later stages without manifesting any symptoms. Even while periodontal disease symptoms are typically subtle, they are not entirely nonexistent. Specific symptoms may indicate a particular form of sickness. Symptoms of gum disease include:
Bleeding gums and red, swollen gums while brushing your teeth and just afterward. Pink and firm gums are indicators of healthy gums. an unpleasant aftertaste or prolonged halitosis Gums with recedes Changes in the way partial dentures fit or how teeth fit together when you bite down,
There are various types of sugar, each with its unique characteristics. Sucrose is the most common in table sugar and naturally in fruits and vegetables. Fructose, primarily in fruits, is the sweetest natural sugar. Glucose, an essential energy source, circulates in our blood. Lactose in milk and dairy products has a less sweet taste. Maltose, from grains and malted foods, is a double sugar unit. High fructose corn syrup (HFCS), a liquid sweetener, is widely used in processed foods and beverages. Understanding these sugar types can help make informed dietary choices and manage sugar intake for better health.
How Can a Dentist Determine if a Patient Has Gum Disease?
During a dental examination, your dentist frequently checks for the following things:
Gum bleeding, edema, stiffness, and pocket depth (the space between the gum and the tooth) all contribute to the condition's severity. Teeth movement, discomfort, and proper tooth alignment. Bone loss surrounding your teeth might be discovered using your jawbone.
What is The Treatment For Periodontal Disease?
Treatment for gum disease seeks to stop the illness's progression and promote the reattachment of healthy gums to teeth. Additionally, it aims to lessen infection risk, pocketing depth, and edema. The stage of the disease influences your treatment options, any past therapy responses, and overall health. Options include non-surgical methods that prevent bacterial growth and surgery to restore supporting tissues. All the therapies that are offered are thoroughly explained in Gum Disease therapies.
How is Gum Disease Prevented?
When effective plaque control is applied, gingivitis can be treated, and gum disease is almost always kept from getting worse. Regular brushing, professional cleanings at least twice a year and flossing are required to control plaque.
Brush your teeth twice a day. Use fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled brush. Replace your toothbrush every three months or sooner if the bristles fall out. They do not clean their teeth even when old and worn out. Plaque is removed from the accessible surfaces of the teeth by brushing. Plaque and food particles are removed from between the teeth and below the gum line with dental floss. Every day, string. It is not recommended to wait until something is between the teeth. The coating is removed from places the toothbrush cannot reach with daily floss. You can also try interdental brushes, interdental brushes, or tiny brushes that fit between the teeth. Ask your dentist how to use them to avoid gum damage. Wash your mouth. In addition to gingivitis, antibacterial mouthwash prevents plaque and bad breath.
According to the American Dental Association, antibacterial rinses can lessen the germs that cause plaque and gum disease. Inquire with your dentist about the ideal mouthwash for you. In addition, you can diminish gum disease's severity and speed up its advancement by making other health and lifestyle changes. They consist of:
Stop smoking
In addition to harming your heart and lungs, smoking can also damage your teeth and gums. Smoking makes some therapies less effective and raises the risk of gum disease in smokers seven times more than in non-smokers.
Decreases Stress
When you're under pressure, your body's immune system could have a more challenging time warding off sickness.
Consume a Nutritious, Balanced Diet
When bacteria in your mouth digest food sugars and starches, acids are formed that erode tooth enamel. There is a lot of added sugar and starch in sweets and fast meals. To keep your teeth and gums healthy, stay away from them. A healthy diet aids the immune system's defense against illnesses. Consuming foods high in antioxidants, including vitamin E, can help your body heal damaged tissues.
Do Not Clench or Clench Your Teeth
These movements can put excessive stress on the tissues supporting the teeth, accelerating tissue decay. According to the American Academy of Periodontology, up to 30 percent of Americans may have a genetic predisposition to gum disease, even if they follow good dental hygiene practices and make other healthy lifestyle choices. In addition, people with a genetic predisposition may have a sixfold risk of developing gum disease. You may be at risk for gum disease if someone in your family already has it.
Your dentist or periodontist may recommend more frequent exams, cleanings, and treatments if you are more likely to develop periodontal disease to manage the problem effectively. Schedule a cleaning to remove plaque and tartar if it has been six months since your last dental visit. Ask your dentist how to brush correctly. Gingivitis can occur due to too solid or missing places. Your gums will heal after the cleaning in about a week if you brush twice daily and floss and rinse once daily.
Gum Disease: Is it Linked to Other Health Problems?
According to the CDC, researchers may have found links between gum disease and other dangerous medical problems. Oral bacteria that enter the bloodstream are usually not harmful to people with robust immune systems. However, these microbes are linked to diseases such as heart disease and stroke under certain conditions. Gum disease is not only a risk factor for diabetes, but diabetes itself can worsen as a result of gum disease.
Overcome Your Gum Disease With Crown Dental Clinic in Coimbatore
Our dentists are here to assist you if you notice any odd bleeding or if your gums are sore. Utilize the dentistry services offered by Crown Dental Clinic in Coimbatore now to take control of your oral health and keep healthy teeth and overall well-being. Gum disorders can be prevented and treated with consistent effort and attention to oral hygiene. Following these five suggestions may significantly reduce your risk of acquiring gum diseases and maintain healthy gums for the rest of your life. Remember that regular dental exams and prompt treatment are necessary to cure gum problems soon.